A groundbreaking study has unveiled a significant link between gut bacteria and the development of fatty deposits in the arteries of the heart. The research, conducted by a team of scientists from renowned institutions, sheds new light on the role of the gut microbiome in cardiovascular health. With heart disease being the leading cause of death globally, this discovery could have far-reaching implications for preventive and therapeutic interventions. This article explores the key findings of the study, delves into the mechanisms behind this association, and discusses potential implications for future treatments.
Table of Contents
The Gut-Heart Connection: Unraveling the Puzzle
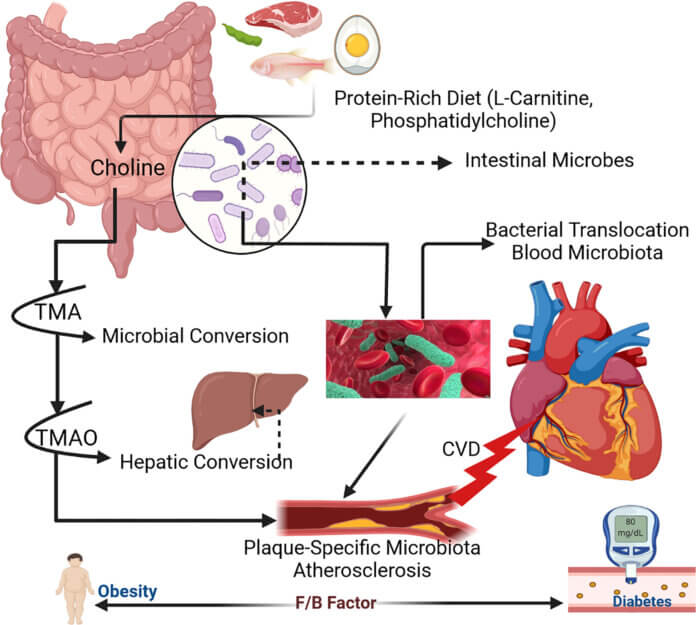
The human gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome. Recent research has revealed the significant influence of this complex microbial community on various aspects of human health. Now, scientists have uncovered a compelling link between the gut microbiome and the accumulation of fatty deposits, known as plaques, in the arteries supplying blood to the heart.
Study Findings: Gut Bacteria and Arterial Plaque Formation
In a comprehensive study published in a leading scientific journal, researchers examined the gut microbiomes of over 1,000 individuals and performed extensive genetic analysis. The results revealed a strong correlation between specific gut bacteria and the presence of arterial plaques. Furthermore, the study identified a subset of bacteria that were consistently associated with a higher risk of plaque formation, independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors such as obesity, smoking, and diabetes.
Mechanisms at Play: How Gut Bacteria Influence Heart Health
Scientists believe that the gut microbiome affects heart health through various mechanisms. One potential pathway is the production of metabolites by gut bacteria that can enter the bloodstream and influence inflammation levels throughout the body. Chronic inflammation plays a crucial role in the formation and progression of arterial plaques. Additionally, certain gut bacteria have been found to produce compounds that contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, the underlying condition responsible for most heart attacks and strokes.
Implications for Cardiovascular Health: A Paradigm Shift
The discovery of a link between gut bacteria and heart artery blockages could potentially revolutionize the field of cardiovascular medicine. It opens up new avenues for preventive strategies, early detection methods, and personalized treatments. By identifying individuals with an increased risk of plaque formation based on their gut microbiome, healthcare providers could implement targeted interventions to prevent the progression of heart disease.
The Promise of Future Treatments: Modulating the Gut Microbiome
Given the newfound association, researchers are now exploring the possibility of modulating the gut microbiome as a therapeutic approach. The use of probiotics, prebiotics, and targeted antibiotics are being investigated as potential strategies to restore a healthy gut microbial balance and reduce the risk of arterial plaques. However, it is essential to conduct further research to determine the most effective interventions and understand the potential risks and limitations associated with manipulating the gut microbiome.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle Factors
Diet and lifestyle choices have long been recognized as significant contributors to cardiovascular health. Interestingly, emerging evidence suggests that these factors may also impact the gut microbiome and, consequently, arterial plaque formation. Unhealthy dietary patterns, high in saturated fats and sugars, have been shown to disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. On the other hand, a diet rich in fiber, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables promotes a diverse and beneficial gut microbiome, which may help protect against the development of arterial plaques.
In addition to diet, other lifestyle factors such as physical activity and stress levels can influence the gut microbiome. Regular exercise has been associated with a more diverse gut microbial community, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease. Conversely, chronic stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, contributing to inflammation and the progression of arterial plaques. These findings highlight the importance of adopting a holistic approach to cardiovascular health by addressing both lifestyle factors and the gut microbiome.
The Gut-Heart Axis: A Two-Way Street
While the recent study focused on the impact of gut bacteria on arterial plaque formation, it is crucial to acknowledge the bidirectional nature of the gut-heart axis. Research suggests that cardiovascular health, including the presence of arterial plaques, can also influence the composition and function of the gut microbiome. Conditions such as high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes, which are closely linked to heart disease, have been associated with alterations in the gut microbial community. Therefore, a healthy gut-heart axis is vital for maintaining overall cardiovascular well-being.
Personalized Medicine and Gut Microbiome Testing
The emerging understanding of the gut microbiome’s role in heart health raises exciting possibilities for personalized medicine. As we delve deeper into the intricate relationship between gut bacteria and arterial plaque formation, it becomes increasingly feasible to develop targeted interventions based on an individual’s gut microbiome profile. Gut microbiome testing could become a valuable tool in assessing cardiovascular risk and tailoring interventions to address specific microbial imbalances.
However, it is essential to approach personalized medicine with caution. The field of gut microbiome research is still in its early stages, and further studies are necessary to establish robust associations and identify reliable biomarkers. Standardized protocols and guidelines for gut microbiome testing and interpretation will also need to be developed to ensure accurate and meaningful results.
Public Health Implications and Future Directions
The discovery of the link between gut bacteria and arterial plaques has profound implications for public health. Incorporating gut microbiome analysis into routine cardiovascular risk assessments could help identify individuals at higher risk of developing heart disease. This knowledge can guide targeted interventions, including dietary modifications, probiotic supplementation, and lifestyle changes, to promote a healthy gut microbiome and reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases on a population level.
Future directions in research include investigating the long-term effects of modulating the gut microbiome on cardiovascular outcomes and exploring the interplay between the gut microbiome and other aspects of heart health, such as heart rhythm disorders and heart failure. Additionally, further studies are needed to unravel the complex mechanisms underlying the gut-heart connection and to determine the optimal strategies for manipulating the gut microbiome for therapeutic purposes.
The Road Ahead: Unanswered Questions and Future Research
While this study represents a significant leap forward in understanding the gut-heart connection, there are still many unanswered questions. Future research endeavors will focus on elucidating the precise mechanisms through which gut bacteria influence arterial plaque formation, exploring the impact of dietary interventions, and conducting large-scale clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of modulating the gut microbiome for cardiovascular health.
Conclusion:
The groundbreaking research linking gut bacteria to the development of fatty deposits in heart arteries offers a fresh perspective on cardiovascular health. With heart disease remaining a global health crisis, understanding the role of the gut microbiome in plaque formation brings new hope for preventive measures and personalized treatments. While further research is needed to unravel the intricacies of this complex relationship, these findings have the potential to reshape our approach to heart disease and improve the lives of millions worldwide.
Image from: frontiersin